What it is about
Learn what corrective maintenance is, how leading fork manufacturer Vetter implements it, and what types of maintenance are an alternative.
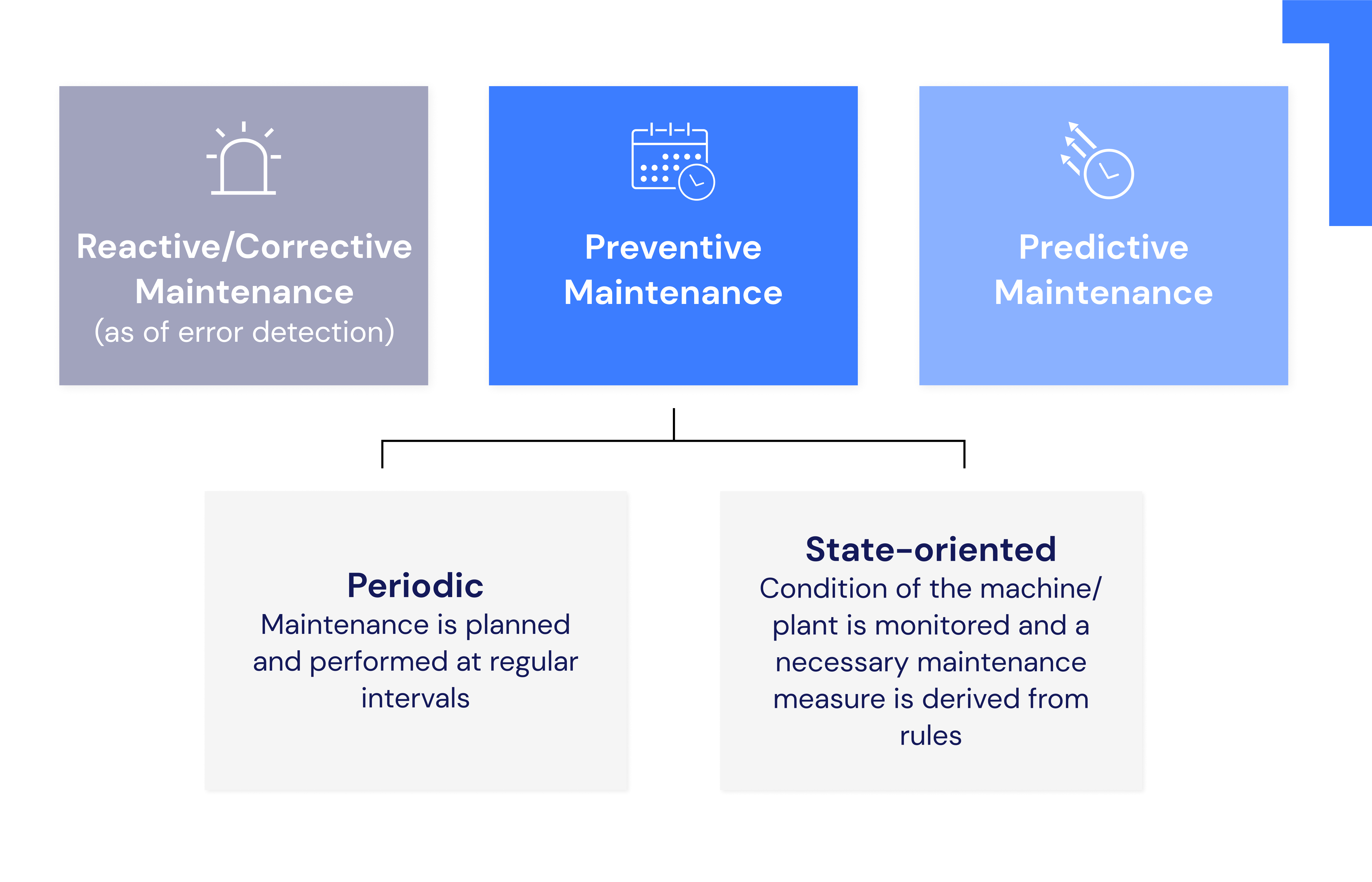
Brief introduction: What is corrective or reactive maintenance?
Corrective maintenance is the servicing of a defective machine to return it to normal operating condition. Corrective maintenance can include deferred and immediate corrective maintenance. Deferred reactive maintenance is maintenance that has not been performed immediately after a fault detection, but has been deferred according to given maintenance guidelines.
When is corrective maintenance recommended?
Corrective maintenance is particularly suitable when a machine failure does not result in significant follow-up costs and repairs or maintenance measures can be carried out without major effort. Otherwise, the approaches of preventive maintenance or predictive maintenance are available. These approaches make it possible to prevent machine failures so that no or fewer corrective measures are necessary.
An example of corrective maintenance: The company Vetter
Our customer Vetter Forks employs about 500 people and produces forks for forklifts. After Toyota, it is the world's leading manufacturer of forks.

Practical example of corrective maintenance
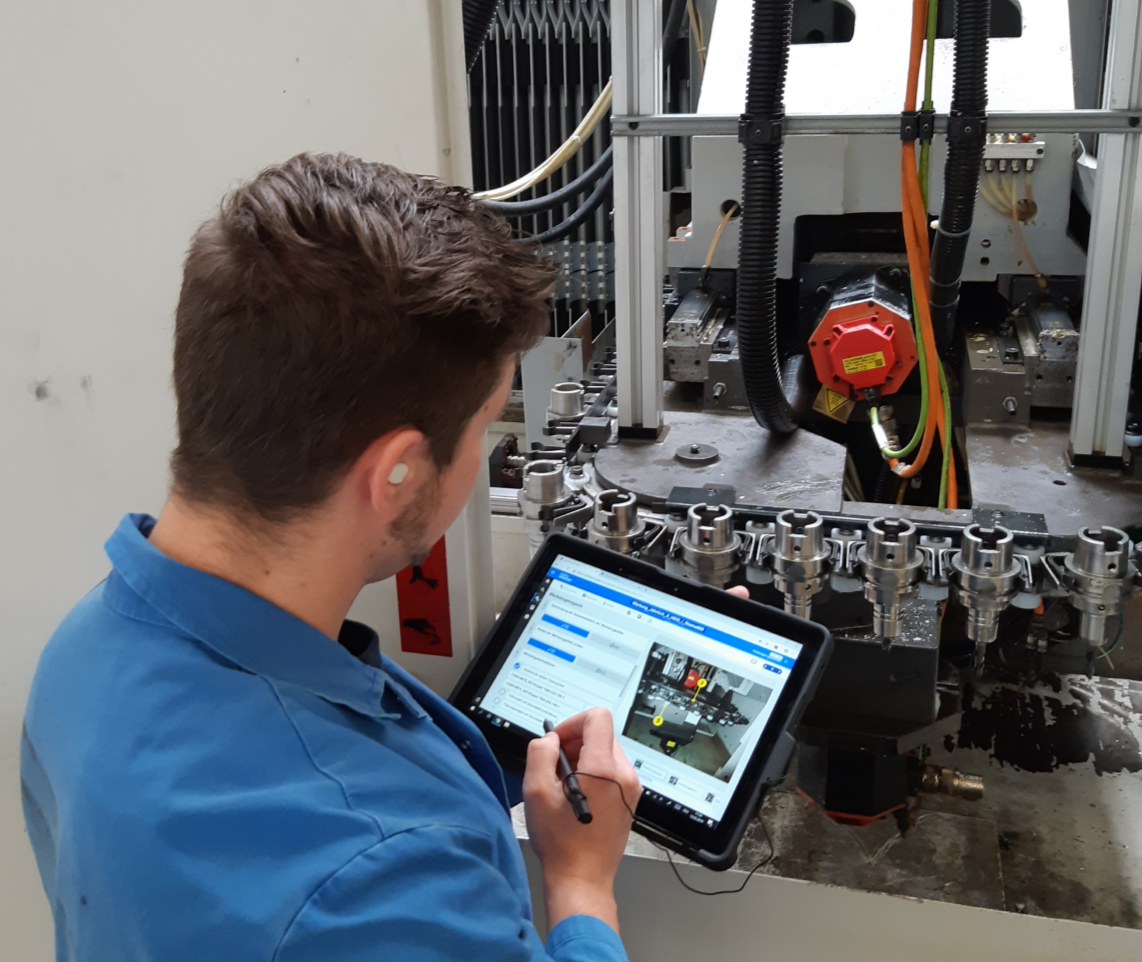
Vetter's maintenance team keeps the production line running. During the course of the day, however, various errors can occur that need to be corrected immediately. To keep track of all faults and follow up on finding solutions, the team needs a suitable digital solution.
Initial situation
Vetter's maintenance team was already working with a digital solution before the introduction of Operations1. The team was using maintenance software that was custom developed by a software agency. However, a software that was not further developed over time. With a lack of improvements and new features, Vetter decided to go with new software that was state of the art. A web-based software-as-a-service product like Operations1 continuously evolves based on cross-enterprise best practices.
Corrective maintenance: The solution with Operations1
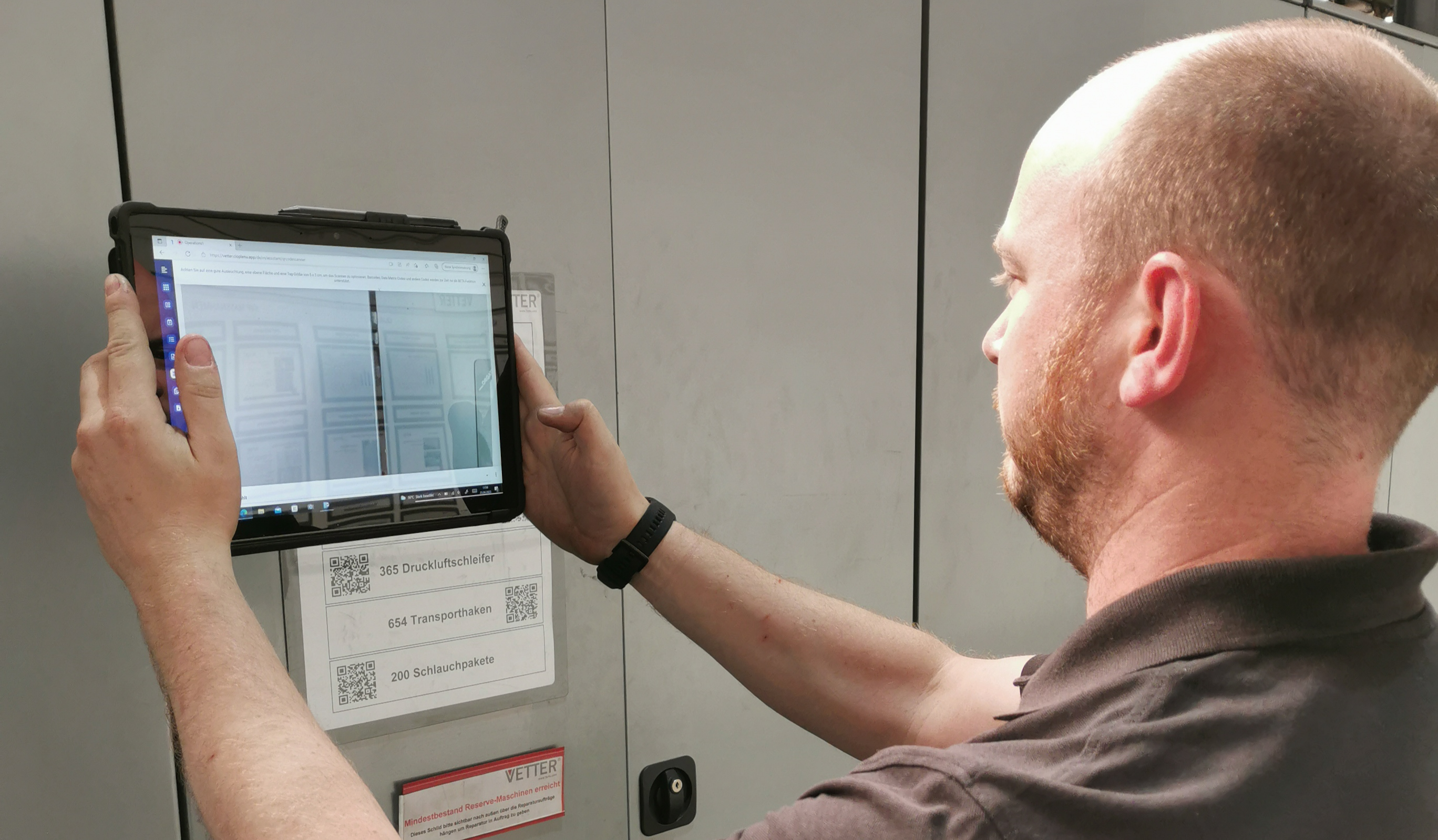
Operations1 software was deployed in a matter of hours. The cloud architecture approach made it easy to roll out the software quickly. Then, the Operations1 customer team worked in partnership with Vetter colleagues to put the use case into production. In the process, Vetter's maintenance team uses Operations1 for all maintenance processes. They use Operations1 on all production areas and in three-shift operation. Fault report management is also handled via Operations1. As soon as the team detects a faulty machine, the process begins:
The maintenance employee scans a QR code near the machine
An incident (task) is created on Operations1
Images, videos, and comments are added to describe the faulty machine and its possible solutions
The task is assigned to a maintenance employee who will lead the resolution process
The progress of the solution-finding process is updated in the task
The entire maintenance team communicates via Operations1 to save time and share knowledge and make the solution-finding process traceable
Once the incident is resolved, the information is updated on the Operations1 dashboard
Vetter's maintenance team now works more efficiently and responds faster to unforeseen incidents. Operations1 helps Vetter manage incidents in real-time and enables collaborative resolution on one platform.

Advantages and disadvantages of corrective maintenance
Advantages of corrective maintenance include:
Lower cost: In the short term, corrective maintenance can be more cost-effective in some cases because you take care of the problem when it occurs. No labor is required to track, monitor and manage machine condition.
Simple process: because corrective maintenance is inherently reactive, it can be a simple solution that requires very little planning or management.
Opportunity to inspect: Completing a corrective maintenance task also provides an opportunity to inspect a piece of equipment due to a failure before a major disruption occurs.
Disadvantages of overusing corrective maintenance include:
Unpredictability: If you only repair a piece of equipment when it breaks, its operation will be highly unpredictable in the long run. In addition, the root causes of the problems are usually not identified and therefore cannot be fixed efficiently. To avoid that, a maintenance plan is the right tool.
Interrupted production: when a critical piece of equipment fails, it can bring your entire production line to a halt, resulting in downtime and unproductive employees.
Shortened equipment life: If you don't take care of your equipment and only perform maintenance when components break, you shorten the overall life of your equipment.
Conclusion
The fork manufacturer Vetter impressively demonstrates a successful use of corrective maintenance through the support of a digital platform. Preventive maintenance approaches are suitable for avoiding incidents.
Get to know the software in just 3 minutes
Discover the functions of Operations1 in an interactive product tour and get to know our platform.

Markus Glotzbach
During his professional career, Markus gained deep insights at companies and large groups in different industries and knows the digitalization hurdles and problems on the shopfloor. Before joining Operations1, he studied International Management (MA) and worked in the Cloud Computing as well as SaaS telematics sector.





