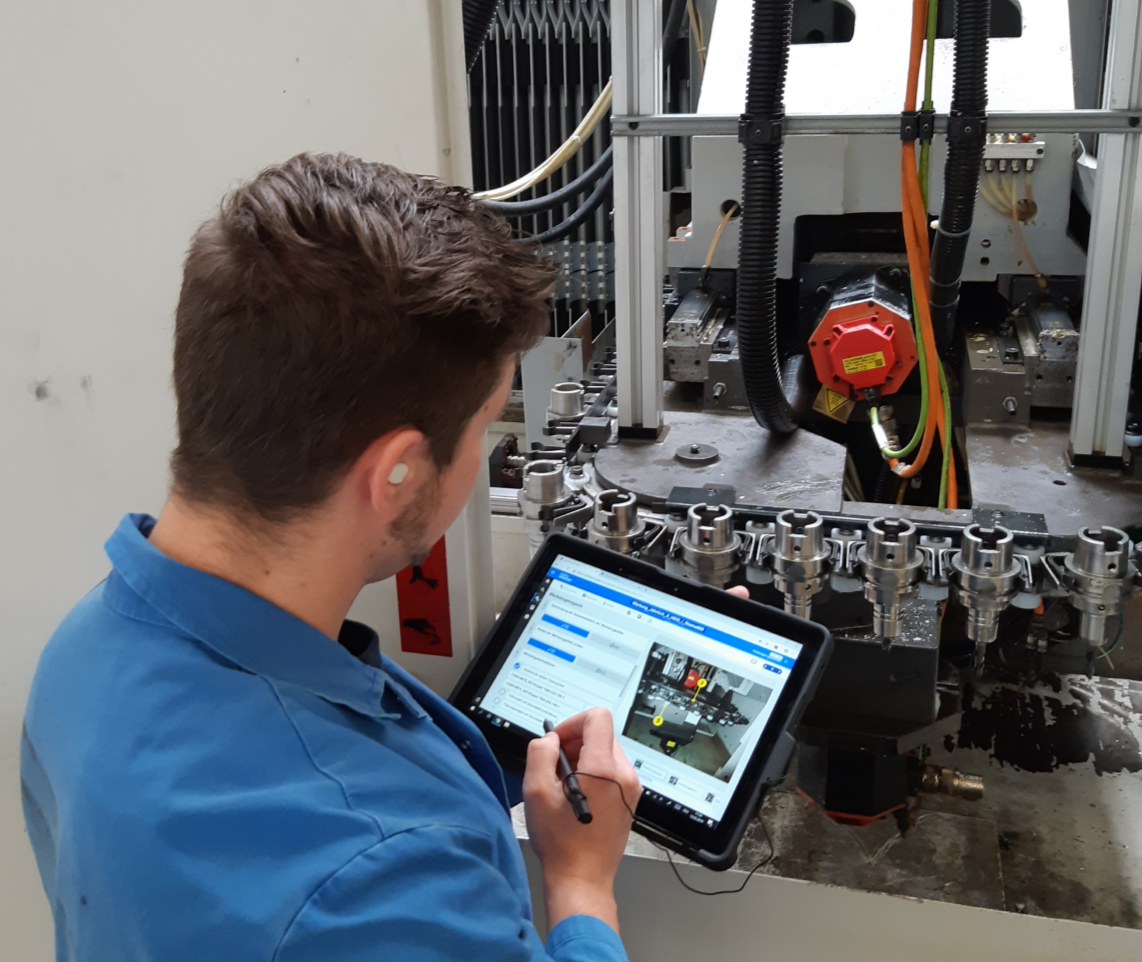
What it is about
In this blog article, we explain the added value of a digital preventive maintenance strategy on the shopfloor.
The following questions are addressed in the blog post:
- What is preventive maintenance, which maintenance concepts are there and which forms of preventive maintenance can be distinguished?
- What are the advantages and disadvantages of preventive maintenance and what implementation tips help?
- What are the disadvantages of paper-based preventive maintenance management?
- Digital preventive maintenance as the key to higher productivity
What is preventive maintenance?
Production is the heart of the manufacturing industry. That is why machine failures and malfunctions as well as unplanned maintenance measures are a worst-case scenario that must be avoided. Maintenance therefore has a special role to play in sustainably increasing effectiveness and productivity.
In so-called "preventive" or "predictive maintenance", maintenance activities are carried out before plant faults or failures occur. The aim is to avoid machine breakdowns and keep maintenance costs for repairs or spare parts as low as possible. Preventive maintenance activities include, for example, inspection and maintenance, preventive repair or replacement, and other preventive measures.
Viewed in a broader context, preventive maintenance is the third of a total of eight pillars of Total Productive Maintenance (TPM). This refers to a concept in maintenance that aims to increase equipment effectiveness and the service life of equipment, thus realizing a production system that is as trouble-free as possible. Effectively optimized, cost-optimized maintenance is intended to eliminate losses and waste so that "zero defects," "zero failures," "zero accidents" and "100 percent quality" are ensured.

Detailed information on the concept of TPM, its origins, the different fields of action as well as advantages and disadvantages, the introduction and digital TPM is provided in our blog post.
Forms of preventive maintenance
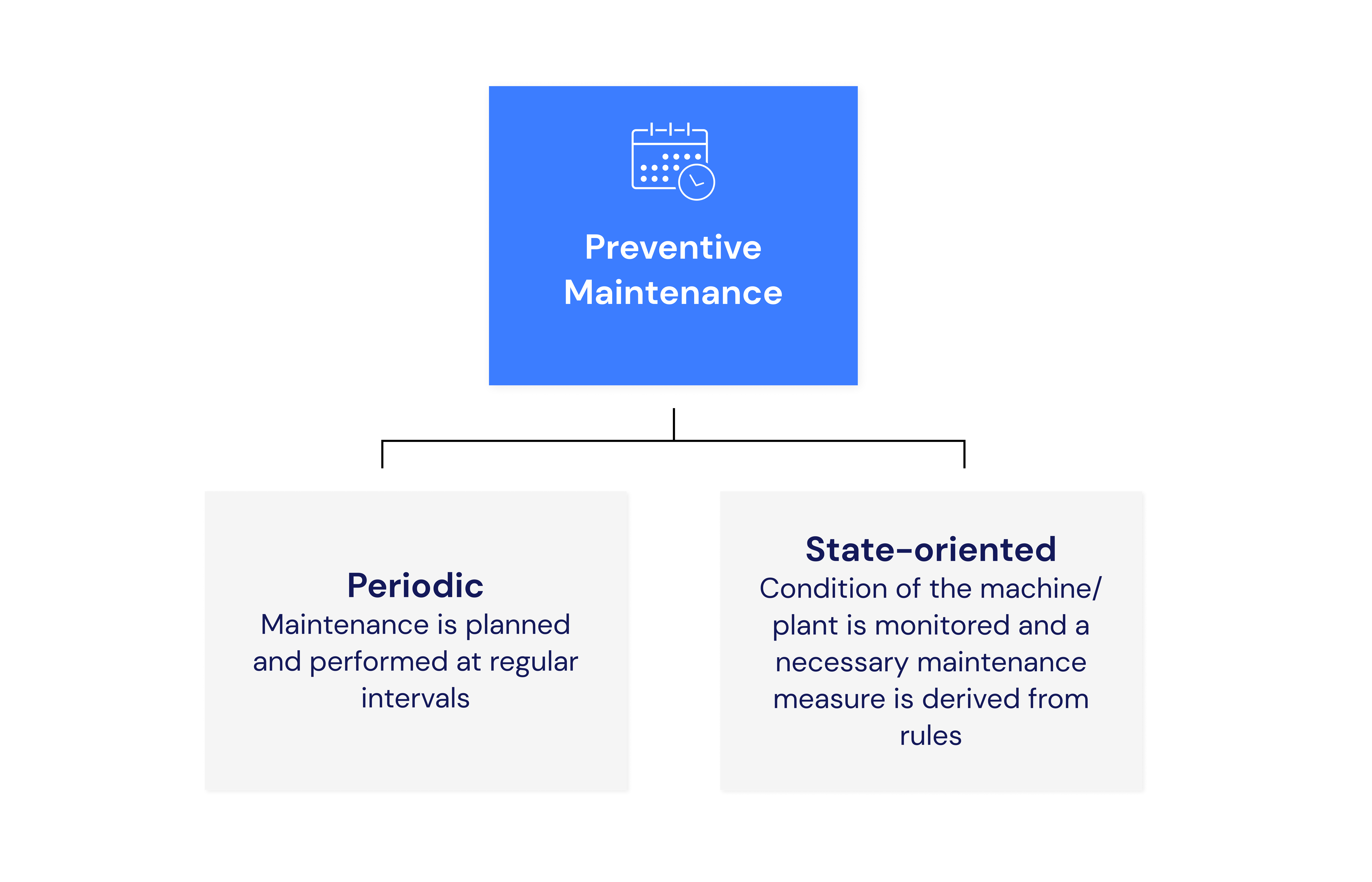
Preventive maintenance is divided into two different forms, each of which is applied in different areas: periodic maintenance and condition-based maintenance. Periodic maintenance is based on maintenance according to a maintenance calendar with intervals according to manufacturer specifications and/or empirical values. It is mainly used for machines that can be replaced and repaired at low cost and for those that rarely break down.
As the name suggests, condition-based maintenance checks the condition of machines in addition to scheduled maintenance, as in periodic maintenance. The aim here is to detect and eliminate sources of error in good time. This is realized either via regular inspections or by means of continuous measurement and recording of parameters such as speed, volume, temperatures, filling levels, pressure or vibrations. These values are then used as physical indicators to determine the condition of the machine and to rectify any deviations from the target condition. For this reason, condition-based maintenance is particularly suitable for machines on which there are many wearing parts. The wear of these parts can then be detected reliably and in good time before major damage occurs.
4 areas of maintenance
According to DIN 31051 and DIN EN 13306, a distinction is made between four basic maintenance measures: Inspection, maintenance, repair and improvement. In order for a company to benefit in the best possible way from maintenance management, it is important that these four areas are closely coordinated. After all, if systematic monitoring of operating equipment and organized and scheduled maintenance are carried out, maintenance measures in the form of repairs are already very low. Nevertheless, repairs cannot be completely avoided by their very nature, because wear and tear and age-related wear and tear are technically and physically part of the process to a certain extent.
Good maintenance management therefore ensures process- and production-optimized maintenance, inspection and servicing, thus ensuring the best possible machine availability.

3 different maintenance concepts
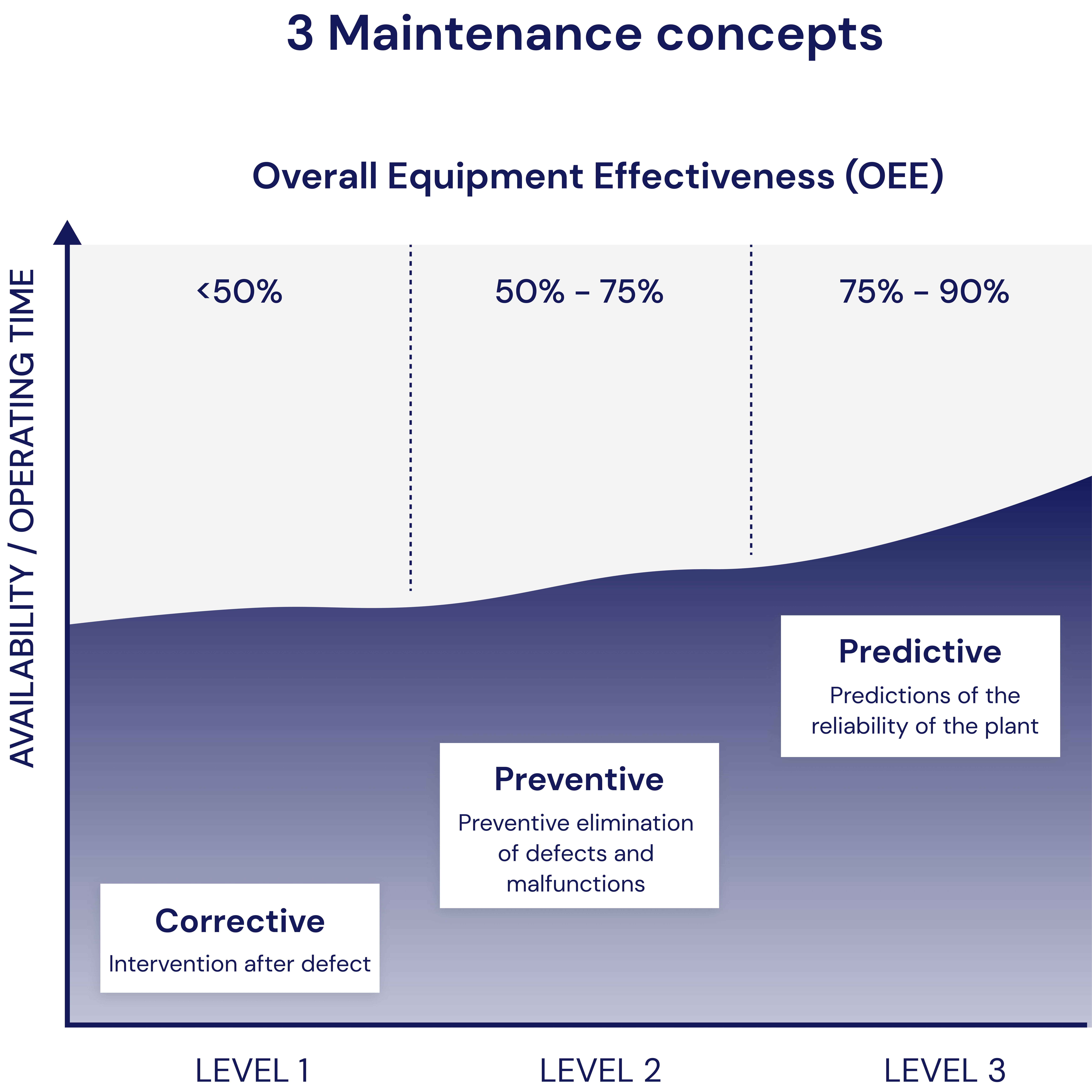
In production, a distinction is generally made between three different maintenance concepts: corrective maintenance, preventive maintenance, which this article is about, and predictive maintenance.
While "corrective" or also "reactive maintenance" is based on the principle of "repairing when something breaks", predictive maintenance follows the approach of "knowing when something will break". An example of a concrete use case of reactive maintenance is given in our blog post about the Vetter company.
Preventive maintenance according to the motto "repair before something breaks" is based on a paradigm shift compared to the corrective maintenance strategy, because the work process is oriented towards a holistic and preventive approach. In general, it can be stated that with a maintenance approach that looks further into the future, the overall equipment effectiveness (OEE) of a machine is significantly extended. The diagram provides a good insight into this relationship.
Advantages and disadvantages of preventive maintenance and tips for implementation
Preventive maintenance with planned maintenance measures according to a specific cycle has numerous advantages over a reactive maintenance approach.
Advantages of preventive maintenance
Avoidance of unplanned downtime and thus higher productivity
Higher work quality and efficiency, as the same work is repeated on a regular basis
Reduction of expensive repair costs thanks to regular maintenance
Better predictability of maintenance and repair
Costs time savings, as the risk of problems occurring in advance is drastically reduced
Longer overall equipment life cycle compared to corrective maintenance
Preventive maintenance is therefore an essential criterion for future-proof, resilient production. Its success can be measured by two key figures: MTTR (= mean time to repair) and MTBF (= mean time between failures). The goal is to minimize MTTR and maximize MTBF.
Disadvantages of preventive maintenance
Despite the many advantages, the preventive maintenance approach also has disadvantages that should be taken into account. These include:
Unnecessary maintenance cycles are likely
Malfunctions cannot be completely ruled out even by predictive maintenance
Higher personnel expenses
Helpful questions when implementing preventive maintenance
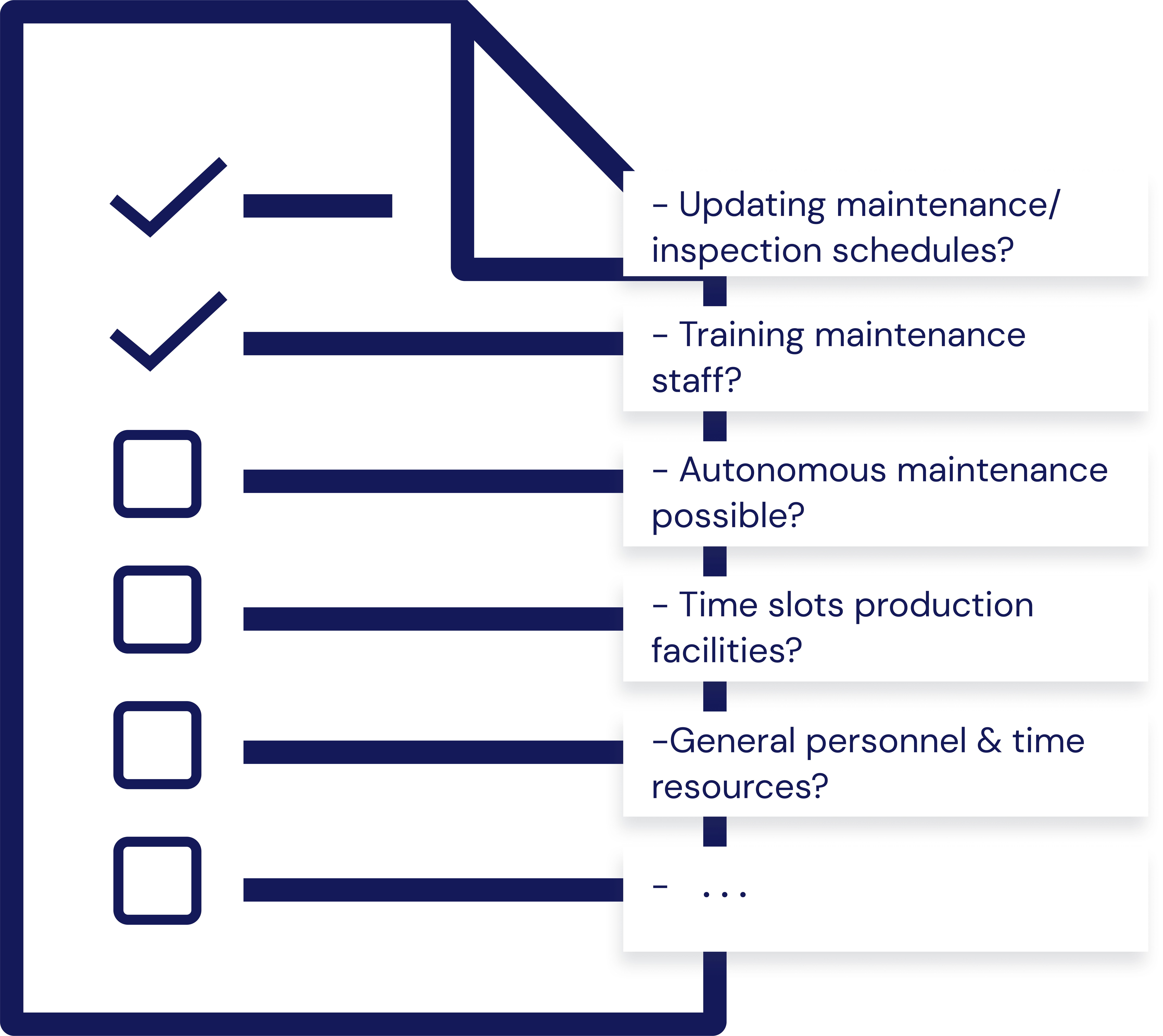
It has certainly become clear that the advantages of preventive maintenance outweigh the disadvantages. For practical implementation, we would like to provide you with the following guiding questions as inspiration and help for placing the topics with your employees:
Who updates and maintains the maintenance and inspection schedules?
Do maintenance personnel need special training?
Can some of the maintenance work also be carried out by production employees in the sense of autonomous maintenance? More details on this concept are explained in our blog post.
In which time slots are the production facilities available for preventive maintenance work?
What personnel and time resources are generally available for preventive maintenance measures?
If you take these and possibly other issues relevant to your company into account when implementing your preventive maintenance strategy, you will always keep the essentials in view.
Disadvantages of paper-based preventive maintenance management
Efficient maintenance planning is essential for the successful implementation of preventive maintenance. However, the problem is that maintenance and service plans have to be created individually and in a time-consuming manner. In many companies, this is done on an Excel basis, which involves a high effort of documentation. In practice, this means that the associated maintenance instructions have to be copied from manuals and expanded in MS Office. This is even more demanding when maintenance checklists and instructions are plant-specific. Post-processing then proves to be resource-demanding and error-prone, and the media discontinuities that occur when manually transferring data from paper to the ERP system cost a lot of time and are often incomplete, so that important information is lost when it is transferred from one medium to another.
Another implication of paper-based preventive maintenance is the lack of traceability over maintenance work performed. This poses a risk during audits or certifications and is especially problematic when traceability is a basic requirement for business relationships, as is common in certain industries. The lack of traceability of data is accompanied by a general lack of transparency. This makes it very difficult for management to correctly assess the current situation and to plan for the future in line with requirements.

Digital preventive maintenance - the key to higher productivity
The challenges faced by manufacturing companies that still operate their production plants without a preventive maintenance software solution are eliminated when they switch to a digital solution.
Advantages of digital preventive maintenance with Operations1
The following advantages are offered by the use of our Connected Worker solution:
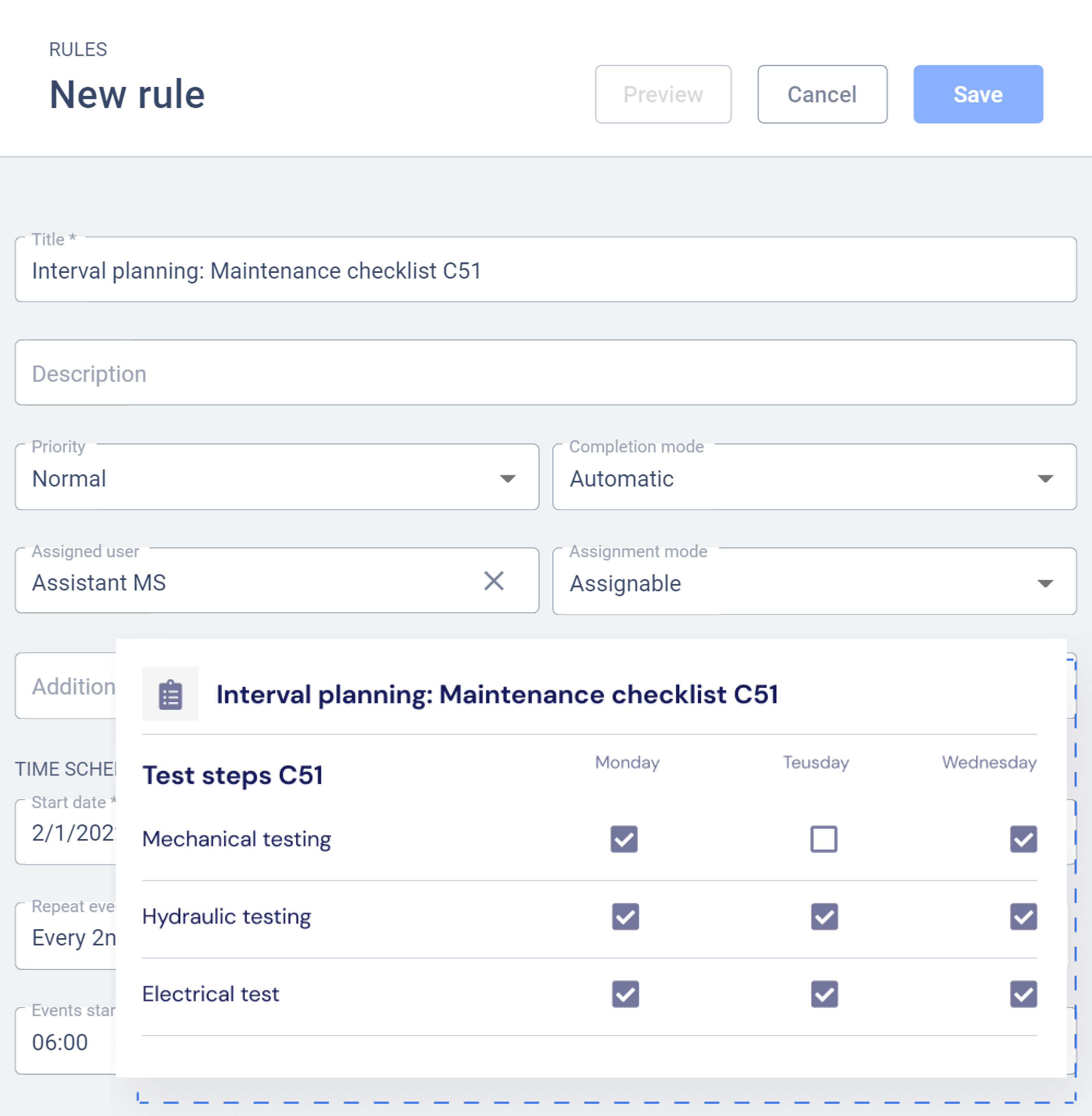
Maintenance plans can be created directly in Operations1 or transferred from ERP, MES or CMMS
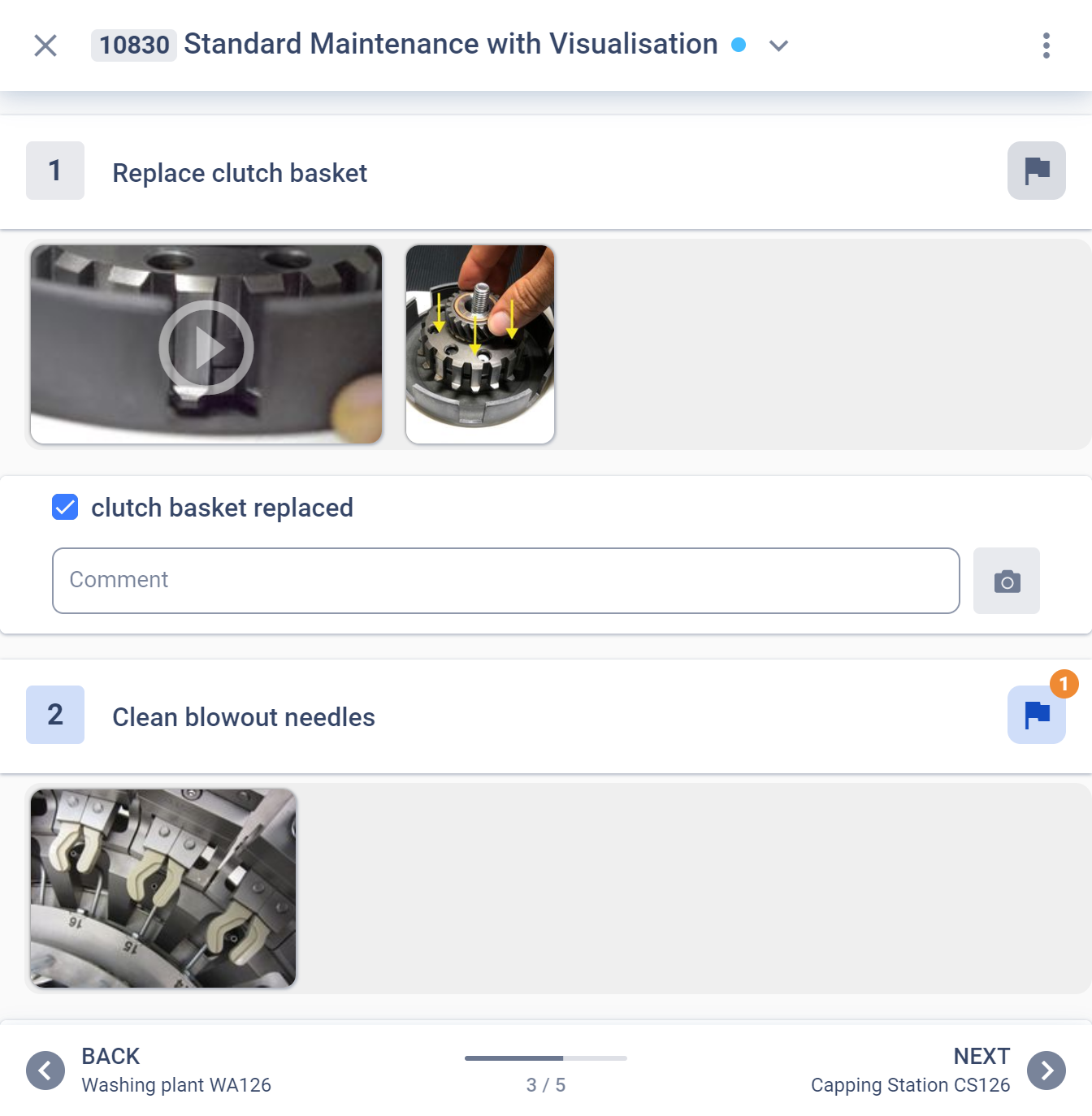
You can provide your employees with intuitive checklists with image- and video-based instructions, thereby also supporting autonomous maintenance activities
Thanks to the possibility of variant configurations individually adapted for you, a high variety of variants can be mapped for systems
Maintenance reports are created automatically
This is the benefit your company derives from digital preventive maintenance with Operations1:
Avoidance of machine breakdowns, high repair and spare parts costs, and documentation activities that do not add value
A more modern and safer working environment for your employees as a result of fewer accidents
More efficient maintenance processes in planning and execution
Higher flexibility in employee deployment through autonomous maintenance
Increased audit security thanks to fully transparent maintenance activities
If you bundle all the advantages offered by digital preventive maintenance on the shopfloor, you can derive several benefits from a digital strategy: Plant availability is increased and, in the long term, the productivity of a company can increase, which in turn lays the foundation for entrepreneurial sustainability. Reason enough to critically rethink a paper-based preventive maintenance approach.
Conclusion: When used correctly, digital preventive maintenance lays the foundation for resilience and operational excellence.
Get to know the software in just 3 minutes
Discover the functions of Operations1 in an interactive product tour and get to know our platform.

Markus Glotzbach
During his professional career, Markus gained deep insights at companies and large groups in different industries and knows the digitalization hurdles and problems on the shopfloor. Before joining Operations1, he studied International Management (MA) and worked in the Cloud Computing as well as SaaS telematics sector.






